This is an old revision of the document!
Blocks
EEROS's control system is mainly made up of blocks. A block can have several inputs and outputs, which carry signals. These signals are transformed from inputs to outputs by the algorithm of the block.
Inputs and Outputs
Every output carries a signal. An input simply refers to a connected output.
 This makes sure that each input is connected to a single output. On the other hand, an output can carry its signal to many inputs.
This makes sure that each input is connected to a single output. On the other hand, an output can carry its signal to many inputs.
Predefined Blocks
Build your control system by instantiating all the necessary blocks. For example:
Step step(0.0, -3.14159265359, 5); step.getOut().setName("phi_desired"); step.getOut().setUnit("rad"); Sum sum; sum.getOut().setName("phi_e"); sum.getOut().setUnit("rad"); Gain posController(174.5); // kp=174.5 posController.getOut().setName("phi_d_set"); posController.getOut().setUnit("rad/s");
Each block has inputs and/or outputs. Name the output in a meaningful way and assign a physical unit to each of the outputs. The signals which connect the different blocks will be created automatically.
The block step is created with an initial output value of 0.0. After 5 seconds this values steps to -pi. step has a single output with the dimension 1.
Output signals are created together with the blocks. On the other side, there is no need to generate and name input signals.
Signals
The signals used to connect the blocks can be different types. Currently the following types are supported
- Real signals
- Logic signals
All signals are vectors of dimension 1…n. Each signal can be assigned a name and a unit. All dimensions of a signal share the same name and unit.
As an example we look at a block which does summation. Two signals, each of dimension 3, will be added together.
Sum sum(3); sum.getOut().setName("phi"); sum.getOut().setUnit("rad");
This is shown in the following diagram:
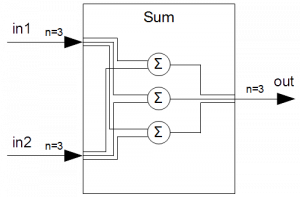
The functions getIn() and getOut() return an input or output signal, respectively. With the summation block, getOut() returns the single output signal. getIn() returns the first input signal. This is the same as getIn(0). To obtain the second input signal you have to write getIn(1). In order to access the individual dimensions of a certain signal, use functions like
sum.getOut().getValue(); // returns dimension 0 of output sum.getOut().getValue(0); // returns dimension 0 of output sum.getOut().getValue(2); // returns dimension 2 of output sum.getIn(1).getValue(2); // returns dimension 2 of input 1
Making Connections
When all necessary blocks have been created the blocks must be wired together.
sum.getIn(0).connect(step.getOut()); sum.getIn(1).connect(enc.getOut()); posController.getIn().connect(sum.getOut());
