Error Handler Usage
The error handler is also a sequence. However, it will be used in case of an exception, so the user knows that it is a recovery pass. To create a new error handler, you have to derive from the class ErrorHandler built in the framework.
class MyErrorHandlerA : public eeros::sequencer::ErrorHandler
Then you can implement the run() method, including all the functionality, to either solve the problem causing the exception or restart the system.
void MyErrorHandlerA::run(){ Reset(); Referencing(); RestartSequence(); }
This run() method will be called in the base class Sequence of the framework if an exception was thrown. The exception is a SequenceException of the framework; it can be thrown at any time. e.g.:
throw new eeros::sequencer::SequenceException(this, static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::MoveException), static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::Initialised), errorHandlerA, false, true, "TestException");
The constructor has following parameters:
SequenceException(Sequence* seqCause, Sequence::method cause, Sequence::method next, ErrorHandler* error, bool toBegin, bool goToNext, std::string reason);
Parameter seqCause und cause: The exception occured in the method cause of the sequence seqCause.
Parameter next: If toBegin is false and goToNext true, then this is the next method on which the sequence continues, after error handling has finished!
Parameter toBegin: Is toBegin true and goToNext false, so the sequence is restarted. (please refer also to the parameter next). Please note: toBegin and goToNext can not be true in the same exception!
Parameter error: error is the ErrorHandler, which defines the behaviour on an exception.
Parameter goToNext: Is toBegin false and goToNext true, then the sequence continues at the next methode after the error handling.
Parameter reason: error message
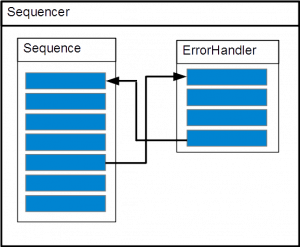
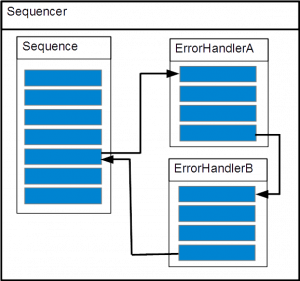
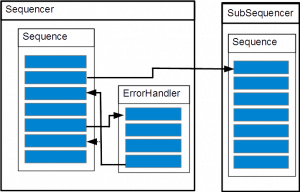
Case 1
exception:
throw new eeros::sequencer::SequenceException(this, static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::MoveException), 0, errorHandlerA, true, false, "TestException");
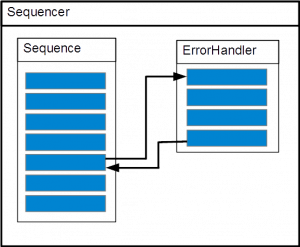
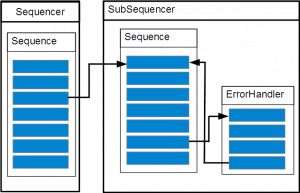
Case 2
exception:
throw new eeros::sequencer::SequenceException(this, static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::MoveException), 0, errorHandlerA, false, false, "TestException");
exception:
throw new eeros::sequencer::SequenceException(this, static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::MoveException), static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::Homed), errorHandlerA, false, true, "TestException");
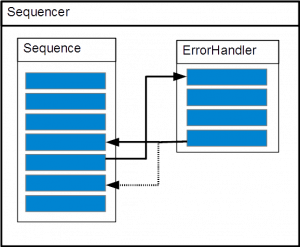
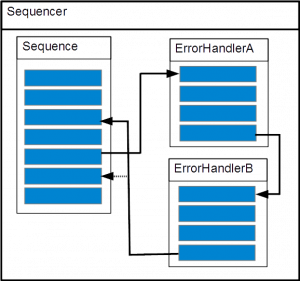
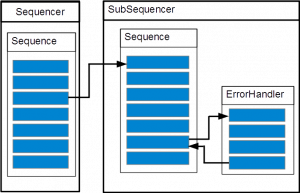
Case 3
exception:
throw new eeros::sequencer::SequenceException(this, static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>&MySequence::MoveException), 0, errorHandlerA, true, false, "TestException");
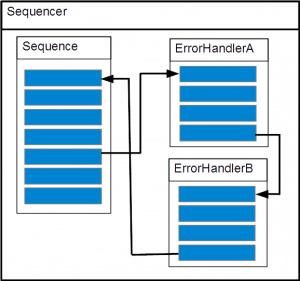
The ErrorHandlerA calls the second error handler ErrorHandlerB.
MyErrorHandlerB* errorHandlerB = dynamic_cast<MyErrorHandlerB*>(eeros::sequencer::ErrorHandler::getErrorHandler("MyErrorHandlerB")); if(!errorHandlerB){ errorHandlerB = new MyErrorHandlerB("MyErrorHandlerB"); } errorHandlerB->run();
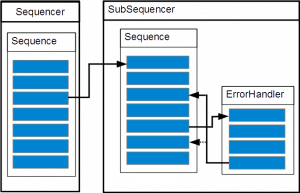
Case 4
exception:
throw new eeros::sequencer::SequenceException(this, static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::MoveException), 0, errorHandlerA, false, false, "TestException");
exception:
throw new eeros::sequencer::SequenceException(this, static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::MoveException), static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::Homed), errorHandlerA, false, true, "TestException");
Case 5
exception:
throw new eeros::sequencer::SequenceException(this, static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::MoveException), 0, errorHandlerA, true, false, "TestException");
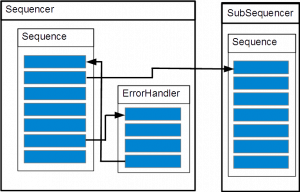
In the case, which the sequencer will be restarted on an exception, the sub-sequencer could be kept on running state or it could also be restarted. This can be choosen by the user. The code below shows how you can solve it.
MySequencer* subSequencer = dynamic_cast<MySequencer*> (eeros::sequencer::Sequencer::getMainSequencer()->findSequencer("SubSequencer")); bool seqIsNew = false; if(!subSequencer){ //use pointer to leave the object in memory!! //without pointer the objetct will be destroyed. subSequencer = new MySequencer("SubSequencer"); seqIsNew = true; //callerThread for NonBlocking Sub Sequence is a new Sequencer //please take attention, if this Object looses scope, so it will be deleted!! //that's why you should use a pointer to allocate memory!! //else the pointer in the Executor runnables list of the Sequencer will point to nowhere!! } NonBlockingSubSequence* subSequence = dynamic_cast<NonBlockingSubSequence*> (eeros::sequencer::Sequence::getSequence("NonBlockingSubSequence")); if(!subSequence){ //MyNonBlockingSubSequence is a Runnable!! subSequence = new NonBlockingSubSequence("NonBlockingSubSequence", *subSequencer); if(seqIsNew){ //now we start the Thread of the subSequencer subSequencer->start(); } } try{ if(!seqIsNew && restartSequencer && subSequencer && subSequencer->getStatus() != eeros::kStopped){ eeros::ExecutorService::waitForSequenceEnd(subSequencer); subSequencer->start(); } }catch(char *str){ }
If restartSequencer is true, so the sub-sequencer will be restarted and you have to wait for the termination of the running sub-sequencer.
If restartSequencer is false, so the sub-sequencer runs until he finished, without restarting.
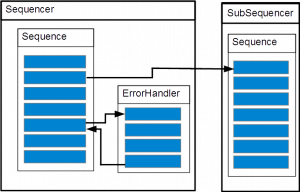
Case 6
exception:
throw new eeros::sequencer::SequenceException(this, static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::MoveException), 0, errorHandlerA, false, false, "TestException");
exception:
throw new eeros::sequencer::SequenceException(this, static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::MoveException), static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::Homed), errorHandlerA, false, true, "TestException");
Case 7
exception:
throw new eeros::sequencer::SequenceException(this, static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::MoveException), 0, errorHandlerA, true, false, "TestException");
Case 8
exception:
throw new eeros::sequencer::SequenceException(this, static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::MoveException), 0, errorHandlerA, false, false, "TestException");
exception:
throw new eeros::sequencer::SequenceException(this, static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::MoveException), static_cast<eeros::sequencer::Sequence::method>(&MySequence::Homed), errorHandlerA, false, true, "TestException");